Ensuring that your learning technology is accessible to all your learners isn’t just a goal — it’s a necessity. Digital learning solutions like learning management systems or learning apps were designed to make learning opportunities easier to access.
But how successful are they in catering to learners with diverse needs? And what can you do to create a digital arena where everyone has a fair shot?
After all, 1.3 billion people across the world experience significant disability. That’s 16% of our total population, or 1 in 6 of us. What’s more, 2.5 billion people need at least one assistive product. This is not an issue that learning professionals can ignore.
Digital spaces are an often overlooked area of accessibility. The web was designed to provide universal access to knowledge. So how is it that just 3.7% of the web is accessible to individuals with disabilities?
Here at Growth Engineering, we believe there should be no barriers to learning. With this in mind, in this article, we’ll explore 14 impactful strategies to make learning technology more accessible and inclusive. But first, let’s start with some definitions.
What is Digital Accessibility?
According to the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C — more on these folks later), digital accessibility means: ‘designing web sites, applications, technologies, tools, products and services in an inclusive manner, and thus lifting barriers to communication and interaction that many people face in the physical world’.
In other words, digital accessibility focuses on making the web accessible to everyone. That includes individuals with a diverse range of hearing, movement, sight and cognitive ability.
As the inventor of the internet, Tim Berners-Lee puts it: ‘The power of the Web is in its universality. Access by everyone regardless of disability is an essential aspect’.
The same holds true of the web-based tools that are used to train staff or educate students. Every learner, irrespective of their unique characteristics, should be able to engage with digital learning environments and educational content seamlessly.
As such, you should take strides to ensure that your digital learning solutions are as accessible as possible. If you can achieve this, both you and your learners will reap the benefits. According to Gartner, digital products that meet level 2 WGAC compliance outperform their market competitors by 50%.
What is Inclusive Design?
Inclusive or universal design is both a mindset and a process. It aims to ensure that a product or solution is usable by as many people as possible, especially those who might typically face exclusion. As such, accessibility is a key outcome for inclusive design.
This design approach considers many different aspects of human diversity, including ability, language, culture, gender and so on. Furthermore, the design process doesn’t just focus on provisioning access to users. It seeks to meet as many of their needs as possible.
Identifying Barriers in Learning Technologies
To understand why learning technology accessibility is important, let’s first examine some common barriers that individuals encounter when learning online.
- Visual Impairment: 2.2 billion people worldwide have visual impairments. This can make navigating a digital learning environment tricky, especially if there’s insufficient support for screen readers or a lack of alternative text for images.
- Hearing Impairment: 1.5 billion people worldwide have hearing impairments. This makes it difficult to consume audio and video content, especially if there are no captions or transcripts available.
- Motor Impairment: According to Inclusive City Maker, 39 million Americans grapple with motor impairments. Learning environments that require precise motor control may pose challenges for these users.
- Cognitive Disabilities: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 12.8% of American adults have a cognitive disability. Overly complex language and training materials may create difficulties for these users.
By addressing these barriers, learning technology can evolve into a tool that empowers learners with diverse needs. In the following sections, we’ll explore ways to overcome these challenges by implementing accessibility measures.
What’s the Impact of Inaccessible Learning Technology?

For those living with disabilities, inaccessible learning environments aren’t a mere inconvenience. They’re a barrier that hinders participation and prevents progress. The effects of this are varied and often debilitating.
If your learning technology is not designed with inclusivity in mind, then a significant portion of your learners will be excluded from educational opportunities. As a result, you’ll perpetuate a cycle of unequal access to information.
And how about the impact on your business? As you might expect, inaccessible learning environments lead to:
- Diminished workforce diversity
- Limited perspectives
- Inequitable skill distribution
All of this has an impact on your ability to innovate, out-compete and boost your bottom line. You can’t build a high-performance learning culture if you’re leaving learners behind and creating knowledge silos.
The Benefits of Accessible Learning Technology
Of course, there’s a flip side to all this. Providing inclusive and accessible learning environments creates a fair playing field. As a result, anyone and everyone has equitable access to information and development opportunities. As you might imagine, this leads to a variety of benefits.
- Expanded Reach: Let’s start with the key benefit. An accessible learning platform empowers you to reach a broader audience of learners, including those with disabilities. As a result, you’ll be able to make an impact in all areas of your organisation.
- Enhanced Experiences: Inclusive design often results in learning experiences that are more intuitive, adaptable and user-friendly. This approach benefits not only individuals with disabilities, but also your broader user-base.
- Elevated Engagement: Expanding your reach and improving your user experience has a knock-on effect. Quality improvements lead to higher levels of engagement. And the more actively engaged your learners are, the more likely they are to change their behaviour.
- Diverse Perspectives: Courting a broader audience also leads to a richer exchange of ideas and perspectives. After all, you’re not excluding anybody from the learning process. This can lead to higher levels of innovation and better financial results.
- Culture of Inclusion: By prioritising inclusive and accessible tech, you’ll help to foster a culture of inclusion, respect and belonging. This sense of community can positively impact the mental health and wellbeing of your learners.
It’s easy to see how all these benefits could have a very real impact on your organisation’s bottom line. For instance, did you know that inclusive teams are over 35% more productive? They’re also 1.7 times more likely to be innovation leaders in their market.
One yet-to-be explored advantage is legal and ethical compliance. That brings us neatly onto our next section.
The Laws and Regulations Governing Web Accessibility
Navigating the web is now part of our everyday lives. According to Statista, we spend six hours and 41 minutes online every day. Much of this time is spent working. In fact, Britons spend 47 days every year using the internet for work purposes.
As a result, governments and regulators across the world have begun to introduce laws and policies that aim to improve levels of digital accessibility. For example, UK web sites are expected to make ‘reasonable adjustments’ to make their site accessible to users with disabilities under the Equality Act 2010.
In the US, government websites are required to meet Section 508 regulations. Commercial websites are covered under the Americans with Disability Act (ADA) Title III. This ‘prohibits discrimination based on disability in places of public accommodation’.
Learning professionals should seek to provide equal access and opportunities for every individual in their audience. You should strive to eliminate barriers and foster an environment where every learner can thrive.
Many of the laws and regulations focused on digital accessibility reference the WCAG standard. Let’s explore that next.
What is the WCAG Standard?
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are an internationally recognised set of recommendations for improving web accessibility. They’re published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), the leading international standards organisation for the internet.
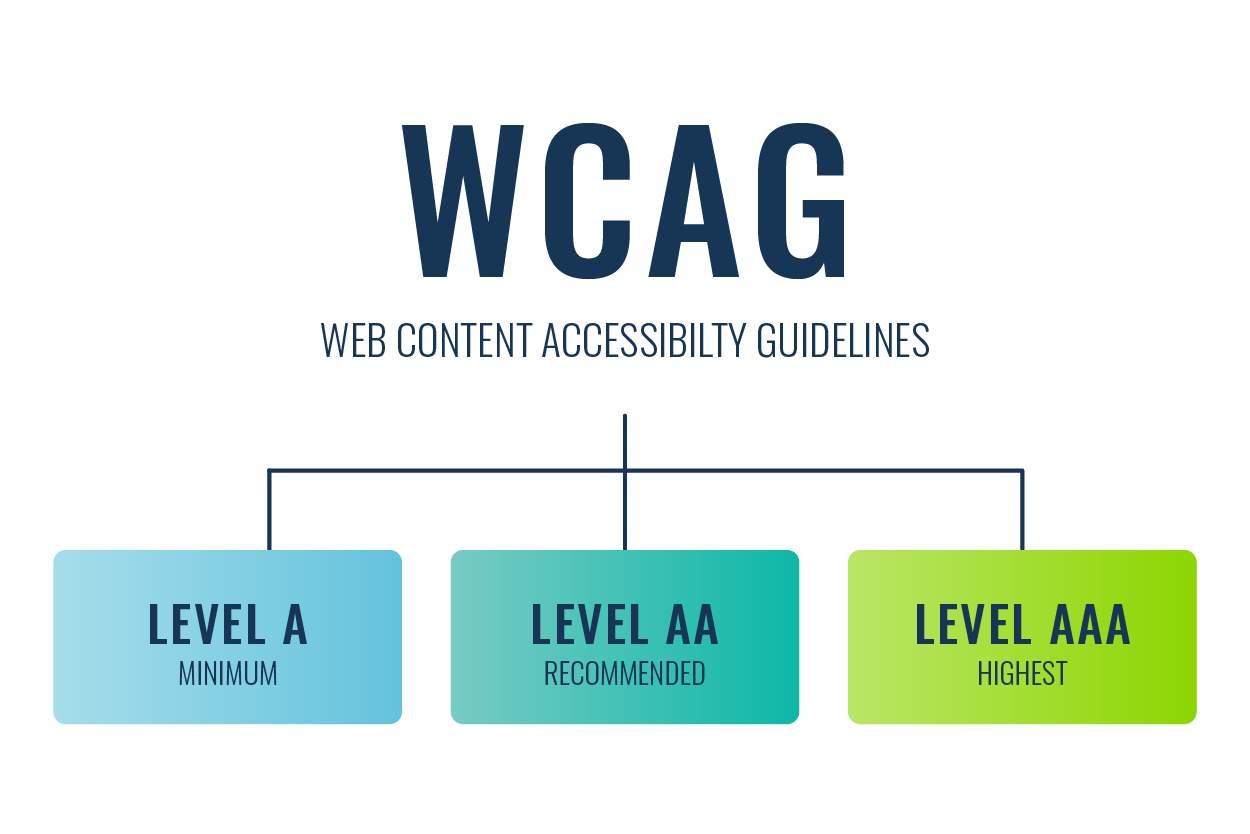
The reach of these guidelines is so extensive that they can safely be considered the benchmark for web site or web application accessibility.
The first version of WCAG was launched in May 1999. The latest version at the time of writing, WCAG 2.2, was published in October 2023. All versions of these guidelines are underpinned by the four following principles:
- Perceivable: Information must be presented in a way that users can perceive. This includes providing alternative text for images, text alternatives for audio, and video captions or subtitles. You also need to make sure that text is easily distinguishable and readable.
- Operable: Users must be able to interact and navigate through your interface effectively and without physical discomfort. You should give your users enough time to read and complete tasks, provide keyboard accessibility and ensure that all navigation actions are consistent and predictable.
- Understandable: There should be no barriers to understanding your content (such as language or complexity) and all navigation elements should be clearly labelled. When completing a form, it should be easy to identify and correct errors. It should also be easy to re-enter information you’ve previously added.
- Robust: Your content must be robust enough to support and be accessed on a variety of devices, including assistive technologies. It should also be compatible with as many operating systems and browser versions as necessary to support your diverse audiences’ needs.
With these principles in mind, consider your digital learning environment. Would your learning management system pass a WCAG audit?
8 Steps to Make Your Learning Technology More Accessible

As we’ve seen, improving the accessibility of your learning technology is crucial for ensuring everyone in your organisation can benefit from educational opportunities. With this in mind, here are 8 ways to make your digital learning environments more accessible.
- Inclusive Design: Design learning platforms and content with inclusive or universal design principles in mind. This helps to accommodate diverse learning styles, abilities and preferences.
- Responsive Design: Ensure your learning platform is responsive and compatible with various devices and screen sizes, including smartphones and tablets. This facilitates learning for users with different access points.
- Multiple Formats: Create learning content in a variety of different formats to better support learners with diverse needs. You have a variety of options to pick from, including text, image, video, audio and so on.
- Captioning and Transcription: Add captions or subtitles to your videos and transcripts for your audio content. This makes them accessible to learners with hearing impairments and benefits those who prefer to read.
- Integrate with Assistive Technologies: Ensure your learning system supports integration with assistive technology such as screen readers, voice recognition software and alternative input devices.
- Accessible Navigation: Review your learning system’s user interface and navigation options. Ensure the structure is easy to follow, the interface is uncluttered and all terminology is clear. Avoid using too many different styles.
- Multi-Language Support: Where relevant, provide multi-language support to cater to a global audience and support learners from different backgrounds. This will increase the reach and scope of your learning initiative.
- Empower Your Learners: Each of your learners has unique needs. As such, they should be able to change their user settings in line with their preferences. This could include text size, colour contrast, screen magnification and so on.
6 Ways to Make Your Learning Initiatives More Inclusive
There’s always more you can do to ensure your learning initiatives are inclusive. By implementing the strategies listed below, you’ll help to ensure that all your learners have access to the same learning opportunities.
- Understand Your Learners: To create truly inclusive learning initiatives, you’ll need to have a deep understanding of your diverse audience. Consider factors such as cultural backgrounds, individual preferences and access to technology.
- Create an Accessibility Statement: Make your commitment to accessibility clear by creating and prominently displaying an accessibility statement. This statement should outline your dedication to providing inclusive learning experiences.
- Use Inclusive Language: Language plays a powerful role in shaping your learning environment and your promotional efforts. Opt for inclusive language that avoids stereotypes, discrimination or unintentional biases.
- Seek Feedback: Regularly check in with your learners to gauge their experiences. Gather feedback on the accessibility of your learning platform and materials, and refine your approach accordingly.
- Embrace Flexibility: Recognise that your learners have diverse needs, schedules and learning preferences. One size does not fit all. Design your learning initiatives with flexibility in mind and let your learners engage in a way that suits them best.
- Offer Support: Ensure all learners have access to further support as and when it’s needed. You should offer resources such as tutorials, help guides and contact points for assistance. Consider implementing peer support or mentorship programmes.
General Accessibility Suggestions
As a learning professional, you may not also be an expert in inclusive design. With this in mind, we’ve included some general accessibility recommendations below. These tips may provide useful guidance for your learning platform.
- Use sans serif fonts (like the one we use here, Open Sans).
- Review your font size and your character, word and line spacing.
- Ensure hyperlinks look different to your other text.
- Avoid background patterns and pictures.
- Use dark text on a light background.
- Add white space around your text and images.
- Include section headers and a table of contents.
- Keep your sentences simple and concise.
- Incorporate bullet points and numbering where relevant.
- Avoid using technical jargon or abbreviations where possible.
Accessibility on Growth Engineering LMS
Here at Growth Engineering, we firmly believe that learning experiences should be open and accessible to all. Growth Engineering LMS, Growth Engineering Learning App and Growth Engineering Authoring Tool have been built with this belief in mind.
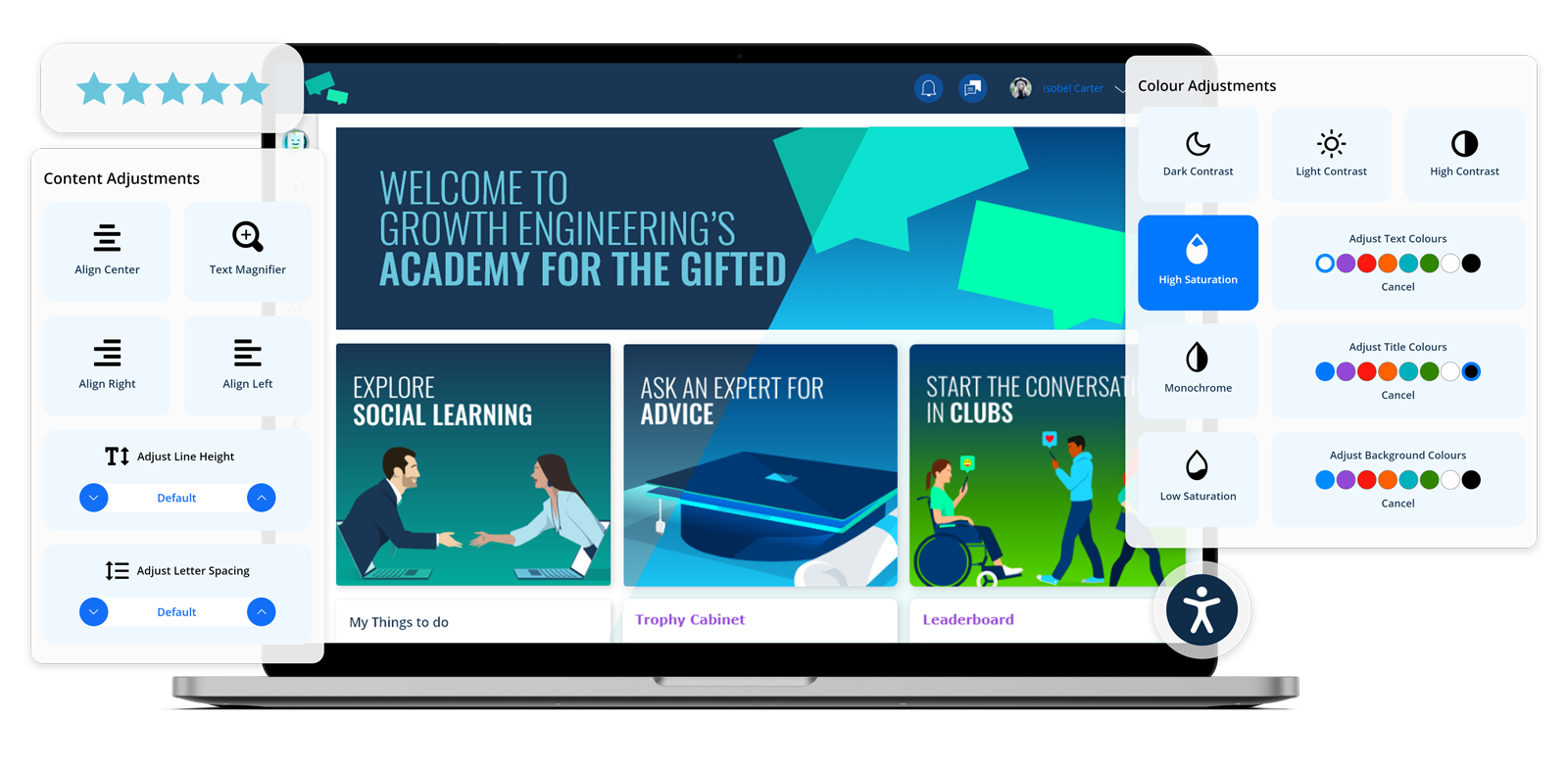
For instance, we utilise an accessibility interface that empowers learners with specific disabilities to adjust the platform’s user interface in line with their personal needs. Learners can select from a variety of accessibility profiles or make the adjustments themselves.
What’s more, learners can navigate through the platform using their keyboard to jump to specific elements. Growth Engineering LMS is also compatible with screen-readers such as JAWS, NVDA, VoiceOver and TalkBack.
That said, we recognise that there’s still more we can do to support learners with diverse needs. As such, we are continually improving our accessibility and updating our solution’s options and features. Watch this space.
Final Words
As technology continues to evolve, the journey towards inclusivity and accessibility is both a responsibility and an opportunity. After all, there are clear benefits to ensuring all your learners have equal access to your learning and development programmes.
Implementing the strategies listed in this guide will help you to create a learning environment where every individual, regardless of their abilities or differences, can thrive.
As such, you should embrace inclusive design, integrate with assistive technologies and seek out feedback from your learners. You should also remember that fostering inclusivity requires ongoing commitment and collaborative efforts.
By championing accessibility, your learning technology becomes a tool for empowerment. Before long, you’ll have a flourishing community, where each and every learner is ready to unlock their full potential. If that’s not a worthy goal to pursue, then what is?
Thank you for reading. Improving accessibility is just one challenge faced by learning professionals. Download ‘The L&D Professional’s Handbook’ now to access 165 tips designed to help you thrive in your job.